
Below are examples of each QR Code Version Level with a table of how much data they can each hold.
The examples below also explain QR Code Versions and what a QR Code Correction Level is
Learn more about the Anatomy of a QR Code here
direct link
Number of modules: 21 x 21

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 25 | 20 | 16 | 10 | |||||
| Example of 25 Characters: QR codes are designed t | |||||||||
Number of modules: 25 x 25

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 47 | 38 | 29 | 20 | |||||
| Example of 47 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in | |||||||||
Number of modules: 29 x 29

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 77 | 61 | 47 | 35 | |||||
| Example of 77 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, an | |||||||||
Number of modules: 33 x 33

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 114 | 90 | 67 | 50 | |||||
| Example of 114 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two | |||||||||
Number of modules: 37 x 37

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 154 | 122 | 87 | 64 | |||||
| Example of 154 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the | |||||||||
Number of modules: 41 x 41

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 195 | 154 | 108 | 84 | |||||
| Example of 195 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors in | |||||||||
Number of modules: 45 x 45

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 224 | 178 | 125 | 93 | |||||
| Example of 224 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the | |||||||||
Number of modules: 49 x 49

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 279 | 221 | 157 | 122 | |||||
| Example of 279 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-de | |||||||||
Number of modules: 53 x 53

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 335 | 262 | 189 | 143 | |||||
| Example of 335 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the fou | |||||||||
Number of modules: 57 x 57

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 395 | 311 | 221 | 174 | |||||
| Example of 395 Characters: QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capa | |||||||||
Number of modules: 61 x 61

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 468 | 366 | 259 | 200 | |||||
Example of 468 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR | |||||||||
Number of modules: 65 x 65

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 535 | 419 | 296 | 227 | |||||
Example of 535 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules ( | |||||||||
Number of modules: 69 x 69

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 619 | 483 | 352 | 259 | |||||
Example of 619 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules (or tiny squares) that make up the code. Version 1, the smallest, consists of a 21x21 | |||||||||
Number of modules: 73 x 73

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 667 | 528 | 376 | 283 | |||||
Example of 667 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules (or tiny squares) that make up the code. Version 1, the smallest, consists of a 21x21 module grid. Each subsequent version adds four | |||||||||
Number of modules: 77 x 77

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 758 | 600 | 426 | 321 | |||||
Example of 758 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules (or tiny squares) that make up the code. Version 1, the smallest, consists of a 21x21 module grid. Each subsequent version adds four modules per side, with Version 40, the largest, comprising a 177x177 module grid. Her | |||||||||
Number of modules: 81 x 81

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 854 | 656 | 470 | 365 | |||||
Example of 854 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules (or tiny squares) that make up the code. Version 1, the smallest, consists of a 21x21 module grid. Each subsequent version adds four modules per side, with Version 40, the largest, comprising a 177x177 module grid. Here’s a breakdown of how the size of the QR code scales with its version number: | |||||||||
Number of modules: 85 x 85

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 938 | 734 | 531 | 408 | |||||
Example of 938 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules (or tiny squares) that make up the code. Version 1, the smallest, consists of a 21x21 module grid. Each subsequent version adds four modules per side, with Version 40, the largest, comprising a 177x177 module grid. Here’s a breakdown of how the size of the QR code scales with its version number:
| |||||||||
Number of modules: 89 x 89

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 1046 | 816 | 574 | 452 | |||||
Example of 1046 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules (or tiny squares) that make up the code. Version 1, the smallest, consists of a 21x21 module grid. Each subsequent version adds four modules per side, with Version 40, the largest, comprising a 177x177 module grid. Here’s a breakdown of how the size of the QR code scales with its version number:
| |||||||||
Number of modules: 93 x 93

| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 1153 | 909 | 644 | 493 | |||||
Example of 1153 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules (or tiny squares) that make up the code. Version 1, the smallest, consists of a 21x21 module grid. Each subsequent version adds four modules per side, with Version 40, the largest, comprising a 177x177 module grid. Here’s a breakdown of how the size of the QR code scales with its version number:
The size increase allows higher versions to store more data. For ex | |||||||||
Number of modules: 97 x 97
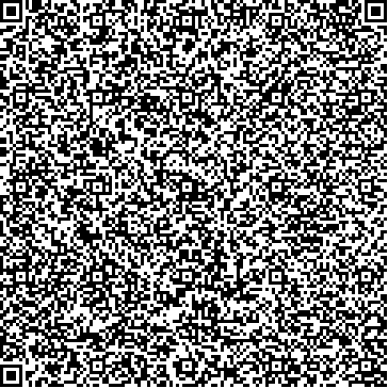
| Correction Level | L | M | Q | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | 1249 | 970 | 702 | 557 | |||||
Example of 1249 Characters:
QR codes are designed to store information in a two-dimensional barcode, and their data capacity depends on two main factors: the version number and the error correction level. These factors influence both the size of the QR code and its resilience to damage. Below is an in-depth explanation of versions 1 through 40 and how the four error correction levels—L, M, Q, and H—affect the capacity and reliability of QR codes.Versions 1 Through 40QR codes come in 40 versions, each determining the number of modules (or tiny squares) that make up the code. Version 1, the smallest, consists of a 21x21 module grid. Each subsequent version adds four modules per side, with Version 40, the largest, comprising a 177x177 module grid. Here’s a breakdown of how the size of the QR code scales with its version number:
The size increase allows higher versions to store more data. For example:
| |||||||||